Hypertension
More than one billion people in the world suffer from hypertension. Its main symptom is high blood pressure. It is generally accepted that normal blood pressure numbers should be lower than 120/80 mmhg. Borderline numbers are between 120/80 and 139/89 mmhg. Blood pressure with numbers greater than 140/90 mmhg is elevated.
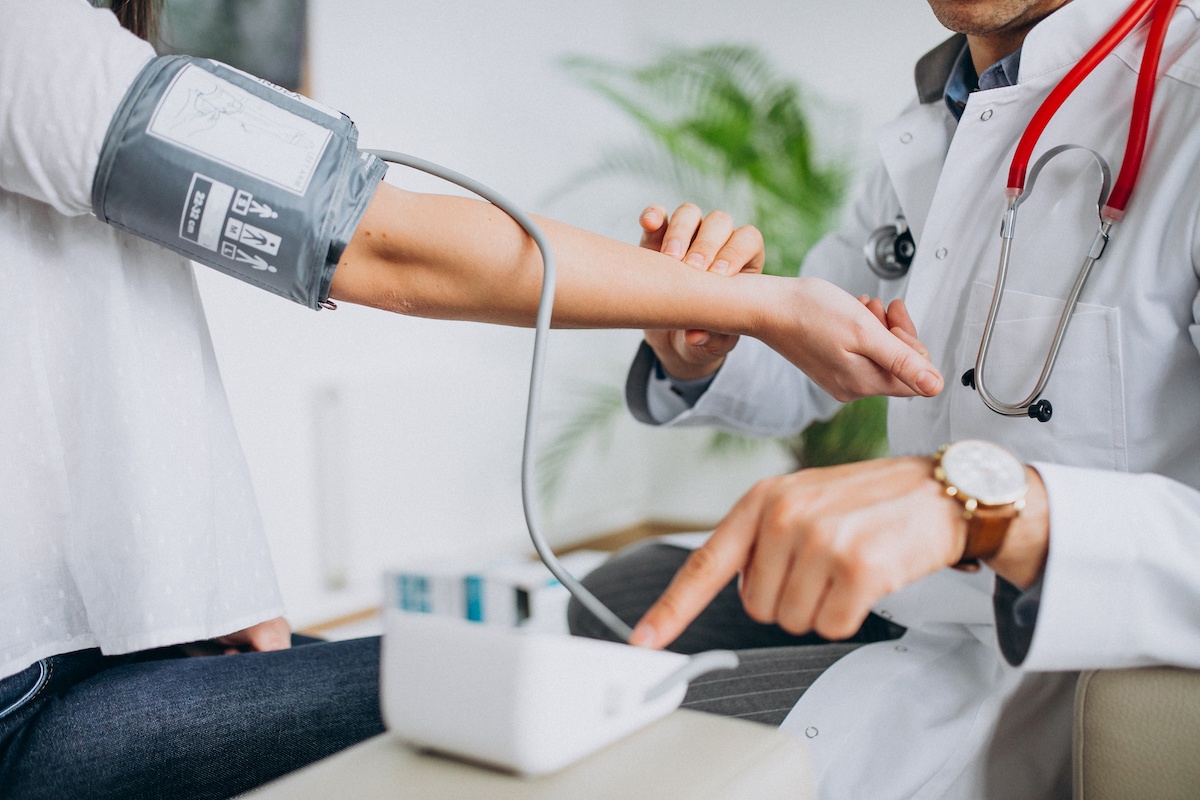
Most physicians arrive at a definitive diagnosis of hypertension when high blood pressure is detected at least twice during three different measurements. It is very important to measure your blood pressure correctly. It is recommended to be in a calm state for 5 minutes before measurement, sitting with lowered legs on a chair; The cuff of the tonometer should fit neatly around the arm. In this position, at least two measurements should be taken.
The auscultatory method of measuring blood pressure (i.e., using a mercury tonometer) remains the most accurate to this day. It is recommended to measure blood pressure at the same time of day and record the results.
Patients with high blood pressure have a significantly increased risk of developing such serious illnesses as cerebrovascular accident, coronary heart disease, kidney and eye complications, heart failure, and sudden death.
Most people with hypertension do not have clinical symptoms, which is why this disease is also called the silent killer. Despite a fairly simple diagnosis and many medicinal possibilities, hypertension continues to win. So, only half of people with high blood pressure are aware of this fact; of these, only half are receiving treatment, and only half of those receiving treatment have their blood pressure stabilized.
Stabilization of blood pressure is extremely important because it reduces the risk of cerebrovascular accident by 40%, the risk of myocardial infarction by 20%, and the risk of heart failure by more than 50%.
The effectiveness of the treatment of hypertension is determined by the degree of reduction in blood pressure. Moreover, in the treatment of different categories of patients, they try to achieve different degrees of pressure reduction. In patients with isolated hypertension, adequate treatment is ascertained at a pressure less than 140/90 mmhg. In patients suffering from hypertension in combination with diabetes mellitus or renal pathology, the optimal pressure is considered to be lower than 130/80 mmhg.
The treatment of hypertension is an art. It includes not only stabilizing baseline blood pressure, but also preventing and reducing risk factors. The nature of the disease is extremely diverse and individual, and the disease itself, once manifested, as a rule, remains forever.
The problem of most patients with essential hypertension is their lifestyle. Lifestyle change is the very first and most difficult step in treatment, and it requires the fulfillment of several extremely important conditions.
The first in this series should be called weight normalization. Weight loss alone may be sufficient to stabilize blood pressure. One-kilogram weight loss is believed to result in a 2 mmHg decrease in upper blood pressure. A weight loss of 5 kilograms, as a rule, leads to a noticeable decrease in pressure in most patients, especially those with mild obesity.
The next important condition is limiting salt intake. Special medical studies have shown that a 5-7mmHg reduction in blood pressure in hypertensive patients was achieved only through a diet low in salt. This diet had more impact on the upper blood pressure numbers, especially in older people with severe hypertension. If someone saltы food before trying it, that is a sure sign that they are over salting it.
A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of developing hypertension. Therefore, patients are encouraged to exercise regularly. According to medical reports, regular exercise lowers blood pressure by an average of 2-4 mmHg. It is recommended that you engage in moderate-intensity physical activity for at least 30 minutes every day.
The next condition is related to alcohol intake. Alcohol can affect blood pressure levels in a number of ways. It directly destabilizes blood pressure, weakens internal control over diet, and reduces the effectiveness of drugs. It is recommended to limit alcohol intake (no more than 50 grams of wine) twice a week for men and once a week for women.
The basis of the treatment of hypertension is a properly selected drug therapy and a well-functioning monitoring and control mechanism. The doctor sets up an individual list of relevant indicators, such as blood pressure, pulse, weight, electrocardiogram, urine protein, electrolyte levels, fundus, etc. The frequency of their checks and the form of feedback are determined. The boundaries (indicators or symptoms) are indicated, going beyond which requires correction of drug treatment, such as a decrease in the resting pulse to 50 or less, an increase in blood pressure to numbers more than 170/110 mmhg or a decrease to numbers less than 90/60 mmhg.
The so-called “red flags” are established – clinical signs of acute complications of hypertension, requiring urgent medical attention. These include chest pain, pain radiating to the back, shortness of breath, sudden severe headache, disorientation, loss of consciousness, difficulty speaking, weakness in the limbs, change in vision, high blood pressure figures that cannot be reduced.
There are many medications that can help lower blood pressure. The doctor determines the treatment regimen. The choice of drugs is carried out individually, taking into account the characteristics of the clinical situation. The choice is influenced by the age, weight, gender of the patient, heart rate, blood pressure level, previous experience of the patient, his psychological state, and the experience of the doctor.
In patients who combine hypertension with another pathology, the choice of drugs is carried out taking into account its effect on the concomitant disease.
In case of ineffectiveness of monotherapy (use of one drug), a second drug is added. The doctor is faced with a difficult task: to build an effective treatment regimen from a combination of a minimum of drugs.
The dosage regimen may allow a certain degree of patient freedom, within the framework established by the doctor. It can be expressed in changing the doses of drugs used depending on the level of blood pressure or pulse, or actions in case of going beyond the boundaries indicated by the doctor. This approach implies the patient’s awareness of the effect of drugs, acceptance of the acceptable framework, and his Compliance.
The success of the treatment of hypertension depends on many factors: changes in lifestyle, serious control over blood pressure, correctly selected medications and a psychological attitude for a long, full life in a real medical situation.